
Cyber security researchers have discovered an updated variant of a thief and malware loader called BunnyLoader which modularizes its various functions and allows it to evade detection.
“BunnyLoader is dynamically developing malware with the ability to steal information, credentials, and cryptocurrency, as well as deliver additional malware to its victims,” Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 said in a report published last week.
The new version, called BunnyLoader 3.0, was announced by its developer named Player (or Player_Bunny) on February 11, 2024, with rewritten modules for data theft, reduced payload size, and improved keylogging capabilities.
BunnyLoader was first documented by Zscaler ThreatLabz in September 2023, describing it as malware-as-a-service (MaaS) designed to harvest credentials and facilitate cryptocurrency theft. It was initially offered on a subscription basis for $250 per month.

The malware has since undergone frequent updates aimed at evading antivirus defenses and expanding its data collection functions, with BunnyLoader 2.0 released by the end of the same month.
The third generation of BunnyLoader goes a step further by not only incorporating new Denial of Service (DoS) features to launch HTTP Flood attacks against a target URL, but also by splitting its stealer, clipper, keylogger and DoS modules into distinct binaries.
“BunnyLoader operators can choose to implement these modules or use BunnyLoader’s built-in commands to load the malware of their choice,” Unit 42 explained.
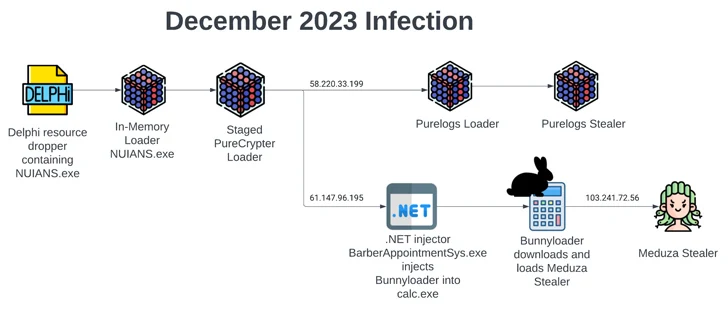
The infection chains that provide BunnyLoader have also become progressively more sophisticated, taking advantage of a previously undocumented dropper to load PureCrypter, which then forks into two separate branches.
While one branch launches the PureLogs loader to finally deliver the PureLogs thief, the second attack sequence drops BunnyLoader to deploy another thief malware called Meduza.
“In the ever-changing landscape of MaaS, BunnyLoader continues to evolve, demonstrating the need for threat actors to regroup frequently to evade detection,” the Unit 42 researchers said.
The development comes in the context of the continued use of the SmokeLoader (also known as Dofoil or Sharik) malware by a suspected Russian cybercrime team called UAC-006 to target the Ukrainian government and financial entities. It is known that it has been active since 2011.
According to an exhaustive report published by the State Cyber Protection Center of Ukraine (SCPC), as many as 23 waves of phishing attacks sending SmokeLoader were recorded between May and November 2023.

“Primarily a loader with additional information theft capabilities, SmokeLoader has been linked to Russian cybercrime operations and is readily available on Russian cybercrime forums,” Unit 42 said.
BunnyLoader and SmokeLoader are joined by two new information-stealing malware codenamed Nikki Stealer and GlorySprout, the latter of which is developed in C++ and offered for $300 for lifetime access. According to RussianPanda, the thief is a Taurus Stealer clone.
“One notable difference is that GlorySprout, unlike Taurus Stealer, does not download additional DLL dependencies from C2 servers,” the researcher said. “Additionally, GlorySprout does not have the Anti-VM functionality found in Taurus Stealer.”
The findings also follow the discovery of a new variant of WhiteSnake Stealer that enables the theft of critical sensitive data from compromised systems. “This new version has removed the string decryption code and made the code easier to understand,” SonicWall said.