
Threat actors are actively exploiting critical OpenMetadata vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to Kubernetes workloads and exploit them for cryptocurrency mining.
That’s according to the Microsoft Threat Intelligence team, which said the flaws have been weaponized since early April 2024.
OpenMetadata is an open source platform that functions as a metadata management tool, offering a unified solution for discovery, observability, and governance of data assets.
The flaws in question – all discovered and attributed to security researcher Alvaro Muñoz – are listed below:
- CVE-2024-28847 (CVSS Score: 8.8) – A Spring Expression Language (SpEL) injection vulnerability in PUT /api/v1/events/subscriptions (fixed in version 1.2.4)
- CVE-2024-28848 (CVSS Score: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in GET /api/v1/policies/validation/condition/
(fixed in version 1.2.4) - CVE-2024-28253 (CVSS Score: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in PUT /api/v1/policies (fixed in version 1.3.1)
- CVE-2024-28254 (CVSS Score: 8.8) – A SpEL injection vulnerability in GET /api/v1/events/subscriptions/validation/condition/
(fixed in version 1.2.4) - CVE-2024-28255 (CVSS Score: 9.8) – An authentication bypass vulnerability (fixed in version 1.2.4)
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability could allow the threat actor to bypass authentication and achieve remote code execution.

The modus operandi discovered by Microsoft involves targeting Internet-exposed OpenMetadata workloads that have been left unpatched to achieve code execution on the container running the OpenMetadata image.
After gaining traction, threat actors were observed performing reconnaissance to determine their level of access to the compromised environment and gather details on network and hardware configuration, operating system version, number of active users and on environmental variables. .
“This reconnaissance phase often involves contact with a publicly available service,” said security researchers Hagai Ran Kestenberg and Yossi Weizman.
“In this specific attack, attackers send ping requests to domains ending in oast[.]I and est[.]pro, associated with Interactsh, an open source tool for detecting out-of-band interactions.”
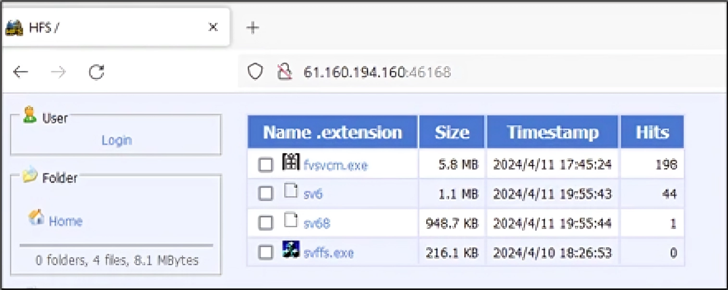
By doing so, the idea is to validate network connectivity from the infiltrated system to the infrastructure controlled by the attackers without raising any alarm bells, thus giving threat actors the security needed to establish command and control communications (C2 ) and deploy additional payloads.
The ultimate goal of the attacks is to retrieve and distribute a Windows or Linux variant of the crypto-mining malware from a remote server located in China, depending on the operating system.
Once the miner is launched, the initial payloads are removed from the workload and the attackers launch a reverse shell for their remote server using the Netcat tool, allowing them to commandeer the system. Persistence is achieved by setting cron jobs to execute malicious code at predefined intervals.
Interestingly, the threat actor also leaves a personal note saying that they are poor and need money to buy a car and a suite. “I don’t want to do anything illegal,” the note reads.
OpenMetadata users are advised to switch to strong authentication methods, avoid using default credentials, and update their images to the latest version.
“This attack serves as a valuable reminder of why it is critical to remain compliant and run fully patched workloads in containerized environments,” the researchers said.
The development comes as publicly accessible Redis servers that have the authentication feature disabled or have unpatched flaws are targeted to install Metasploit Meterpreter payloads for post-exploitation.

“When Metasploit is installed, the threat actor can take control of the infected system and even dominate an organization’s internal network using the various features offered by the malware,” the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) said.
It also follows a report from WithSecure detailing how search permissions on Docker directories could be abused to achieve privilege escalation. It is worth pointing out that the issue (CVE-2021-41091, CVSS score: 6.3) was previously reported by CyberArk in February 2022 and fixed by Docker in version 20.10.9.
“Setting the searchable bit for other users on /var/lib/docker/ and subdirectories may allow an attacker with limited privileges to gain access to the filesystems of various containers,” WithSecure said.